Advertisement
In the summer of 2023, just as regulators sharpened their knives to challenge Google’s dominance over search and advertising, something curious happened. The spotlight shifted. Public debates pivoted away from lawsuits and hearings toward generative AI, large language models, and the rise of chat-based search.
Suddenly, Google wasn’t just a monopolist—it was a pioneer, battling OpenAI and Microsoft in a race to define the future of information. AI didn’t just reshape Google’s products. It shifted the entire narrative. But while this technological pivot may have softened regulatory pressure, it raises a harder question: what exactly did Google give up to hold on to its crown?
For years, Google sat at the center of global antitrust scrutiny. From the EU’s multi-billion euro fines to the U.S. Department of Justice’s lawsuit in 2020, regulators accused the company of abusing its market dominance—especially in search, advertising, and mobile operating systems. The argument was familiar: Google used its control over Android and its search engine to crowd out rivals, direct traffic inward, and protect its revenue streams.

By early 2023, the situation had escalated. A trial loomed in the U.S. to determine whether Google’s search contracts with Apple and others constituted illegal monopolistic behavior. Internally, the company faced growing unease. Advertising made up over 80% of its revenue, and any shakeup in default search placement could shatter that model. In short, the company needed a shift in the narrative, fast.
And then AI exploded into public consciousness. OpenAI’s ChatGPT lit a fire across the tech industry. Microsoft quickly moved to embed OpenAI’s tech into Bing, and for the first time in years, it seemed like a real search competitor had emerged. Google responded by rushing out Bard (now Gemini), a generative chatbot layered on its search infrastructure. The timing couldn’t have been better. Suddenly, regulators weren’t debating Google’s old search monopoly—they were watching a new race unfold.
In public and behind closed doors, Google leaned heavily into AI as a strategic counterweight. It signaled that the future of search was up for grabs again. It wasn't about fixed blue links anymore, but fluid, generative conversations. If anything, the company argued, AI introduced more competition, not less.
The Justice Department’s case against Google became harder to frame in simple terms. If Microsoft’s Bing had access to OpenAI and could generate answers that rivaled or surpassed Google’s, was the company still gatekeeping the internet? And if search was evolving into AI-driven interaction, should yesterday’s antitrust frameworks even apply?
This reframing proved effective. Headlines stopped calling for Google’s breakup and started asking whether the company could keep up with innovation. News cycles moved on. Political pressure cooled. Even some regulators softened their tone, seeing AI as an equalizing force.
But Google didn’t just win time. It also bought cover to preserve its business model—at least on the surface.
Behind the PR wins and the public demos, the cost of AI’s rollout was steep. To avoid becoming the next Nokia, Google pushed AI integration at a breakneck pace. Bard was released before it was ready. Employees flagged its poor accuracy and missteps early on, but launch dates were set based on competitive pressure—not product confidence.

Many inside the company, especially those from Google’s once-respected AI ethics teams, saw the shift as alarming. Years of careful research on fairness, bias, and misinformation were deprioritized in favor of quick iterations. Some senior researchers resigned. Others were pushed out. A company that once led the AI safety conversation found itself cutting corners to catch up.
There were technical compromises, too. Google Search, still the company’s core product, began to show AI-generated summaries alongside or above traditional links. These snippets often gave incorrect or misleading answers, something critics quickly pointed out. Google had spent two decades tuning its search results for trust and relevance. AI summaries—opaque and unpredictable—risked unraveling that work.
And then came the financial strain. Training large models, such as Gemini, and running them at scale is expensive. Google's data centers were already power-hungry. Adding generative AI on top multiplied the cost. Investors began to question whether AI, in its current form, could ever match the profitability of keyword advertising.
Ironically, the very thing that shielded Google from antitrust action—its AI push—may threaten the business fundamentals regulators couldn’t touch.
For now, Google has sidestepped a breakup. But it hasn’t escaped the deeper reckoning. AI bought it time, not safety. The company now faces a different challenge: adapting its empire to a new information economy without collapsing under its own speed.
It must figure out how to integrate generative AI without cannibalizing search revenue. If users get full answers from chat, they may stop clicking links. That undercuts advertising—Google’s profit engine. The company also needs to restore trust after early AI missteps, which won’t be easy with so many products now powered by machine learning.
Regulators are adjusting. New hearings focus less on market share and more on how AI could concentrate power differently—through access to training data, chipmaker partnerships, and control over platforms like Android and Chrome. Google isn’t off the hook. The rules are just being rewritten.
There’s a quieter cost, too. Google once stood for careful innovation—a place where engineers could take time, build responsibly, and earn user trust. The AI arms race has changed that. Speed, secrecy, and survival now rule.
Some at the company worry the shift is irreversible. They’re not wrong to ask whether avoiding a courtroom fight came at the cost of what made Google matter.
AI may have saved Google from an antitrust breakup, but it pushed the company into new turmoil. While it escaped legal threats, Google now faces eroding trust, rushed innovation, and ethical compromises. Its dominance in search remains, yet the rise of AI is redefining that power. The technology that secured its survival could ultimately reshape—or even weaken—the company’s future if balance and accountability continue to slip.
Advertisement
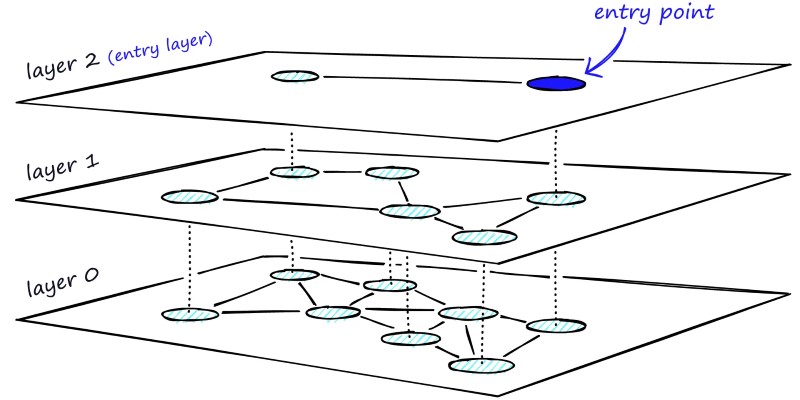
Learn how HNSW enables fast and accurate approximate nearest neighbor search using a layered graph structure. Ideal for recommendation systems, vector search, and high-dimensional datasets

How AI is changing the future of work, who controls its growth, and the hidden role venture capital plays in shaping its impact across industries
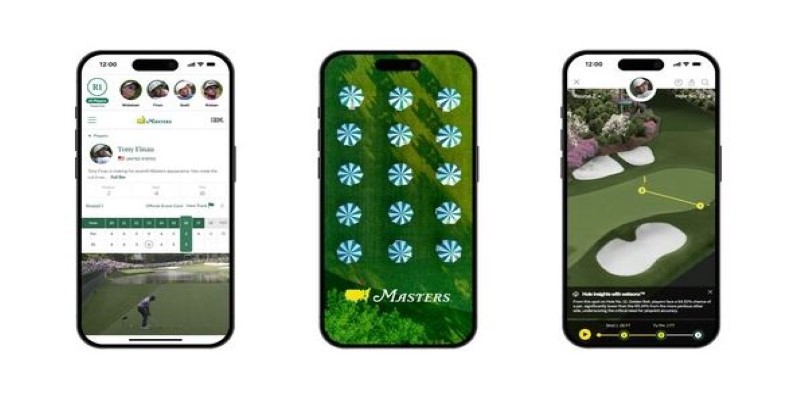
How IBM expands AI features for the 2025 Masters Tournament, delivering smarter highlights, personalized fan interaction, and improved accessibility for a more engaging experience

How MPT-7B and MPT-30B from MosaicML are pushing the boundaries of open-source LLM technology. Learn about their architecture, use cases, and why these models are setting a new standard for accessible AI

AI saved Google from facing an antitrust breakup, but the trade-offs raise questions. Explore how AI reshaped Google’s future—and its regulatory escape

How does an AI assistant move from novelty to necessity? OpenAI’s latest ChatGPT update integrates directly with Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace—reshaping how real work happens across teams

Nvidia is set to manufacture AI supercomputers in the US for the first time, while Deloitte deepens agentic AI adoption through partnerships with Google Cloud and ServiceNow

How using open-source AI models can give your startup more control, lower costs, and a faster path to innovation—without relying on expensive black-box systems
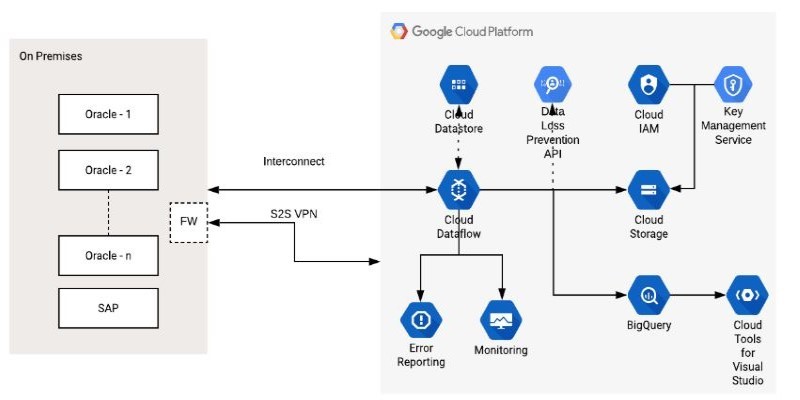
How the Google Cloud Dataflow Model helps you build unified, scalable data pipelines for streaming and batch processing. Learn its features, benefits, and connection with Apache Beam

AI-first devices are reshaping how people interact with technology, moving beyond screens and apps to natural, intelligent experiences. Discover how these innovations could one day rival the iPhone by blending convenience, emotion, and AI-driven understanding into everyday life

An AI health care company is transforming diagnostics by applying generative AI in radiology, achieving a $525M valuation while improving accuracy and supporting clinicians

How the Model-Connection Platform (MCP) helps organizations connect LLMs to internal data efficiently and securely. Learn how MCP improves access, accuracy, and productivity without changing your existing systems