Advertisement
It’s not often that a tool designed for general use starts speaking fluently in the language of business, but that’s exactly what ChatGPT has done. With its latest update, OpenAI signals something loud and clear: it’s serious about making ChatGPT a fixture in the workplace. This isn’t about bells and whistles; it’s about quietly reshaping how work gets done. The new integration with enterprise platforms like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace goes beyond convenience—it speaks to the growing role AI plays in day-to-day tasks.
When ChatGPT was first launched, most people saw it as a clever assistant for brainstorming or casual help. Maybe you asked it to write a message, fix grammar, or summarize a meeting. But the new direction is different. OpenAI is pushing it from a helpful companion to something that blends into existing work tools—calendars, emails, spreadsheets—and works alongside people in real time.
This shift doesn’t come out of nowhere. Businesses today are looking for ways to streamline communication, reduce context-switching, and cut the time spent jumping between apps. Instead of toggling between a document, an inbox, and a planning tool, what if one AI assistant could operate inside them all, offering quick help exactly where it's needed?
That’s what OpenAI is aiming for. By weaving ChatGPT directly into Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, it becomes something employees use without thinking about it. You’re in Gmail writing a tricky message? ChatGPT is right there. You’re in a spreadsheet trying to make sense of scattered numbers? It’s already on it. This isn't a tool that waits to be called—it's present, it's ready, and it quietly removes friction.
OpenAI’s update includes several things designed to make ChatGPT more useful in business settings, but a few stand out more than others.

Workspace Integrations: The upgrade allows direct access to files and apps within Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. That means the assistant can read, summarize, and edit documents stored in Drive or OneDrive. No more downloading, uploading, or copying—ChatGPT can just read the doc where it is.
Memory Capabilities for Teams: While memory was once a personal feature for individual users, OpenAI has extended it to team accounts. Now, ChatGPT can remember team-specific preferences, workflows, and prior conversations. It’s like onboarding a new colleague who never forgets what happened in the last meeting.
Admin Controls and Centralized Billing: For IT teams, this upgrade brings more control. Administrators can manage who gets access, view usage reports, and handle billing in one place. This makes ChatGPT less of a rogue tool used by a few and more of a company-wide resource.
Custom GPTs for Internal Use: The ability to build and deploy company-specific GPTs means businesses can fine-tune the AI for internal tasks. A custom assistant that understands your internal jargon, your team structure, and your workflows? That’s no longer a fantasy.
Let’s break down how businesses can begin integrating ChatGPT into their daily routines using this upgrade. It’s not about starting from scratch—it’s about letting the AI slot into what's already happening.
Once a company account is set up, teams can connect ChatGPT to their Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace. This connection allows the AI to access calendars, documents, sheets, and emails. It’s not just about reading files; it’s about working with them. For example, a manager can ask ChatGPT to “summarize the last three reports stored in Drive” or “draft an email based on this spreadsheet.”
Now that ChatGPT has team-level memory, companies can train it on internal routines and language. If your business calls a weekly planning meeting a “Monday Sync,” the assistant will start referring to it the same way. If your team typically uses a specific file template, the AI will learn to start with that layout. This reduces the back-and-forth of explaining context repeatedly.
Through OpenAI’s GPT Builder, teams can create custom versions of ChatGPT that specialize in different internal tasks. A customer support GPT can be trained on past tickets. A finance assistant GPT can be fed company-specific expense policies. This isn’t just personalization—it’s specialization, built with company data.
With centralized admin features, companies can decide who uses ChatGPT and how. IT teams can roll out the tool slowly, test it within departments, and scale from there. They also get visibility into what it’s used for—helpful for understanding value and identifying areas to improve.
There’s a quiet efficiency that comes from not needing to think about tools too much. When software blends into your daily habits instead of demanding your attention, it changes how you approach work. This is what OpenAI is hopeing that people don’t need more software, they need smarter support inside the software they already use.

And it's not just the big gestures. It's the everyday stuff. A marketer juggling multiple projects can get a content summary without leaving their inbox. A project manager can review meeting notes automatically generated from documents already shared in Drive. None of this requires extra effort, but it adds up over time.
That’s the real change here: not new capabilities in a vacuum, but context-aware assistance. The kind that adjusts to you, instead of the other way around.
OpenAI isn’t just making ChatGPT better—it’s making it work like a teammate. This upgrade isn’t about flash or spectacle. It’s about making the things you already do easier, faster, and less tiring. And that’s something businesses of every size are paying attention to.
By slipping into existing platforms and helping where help is needed most, ChatGPT takes a quiet but confident step toward becoming part of the workplace fabric, not in a showy way, but in the kind of way that makes you wonder how you ever got things done without it.
Advertisement

Watsonx AI bots help IBM Consulting deliver faster, scalable, and ethical generative AI solutions across global client projects
Nvidia NeMo Guardrails enhances AI chatbot safety by blocking bias, enforcing rules, and building user trust through control

Discover the latest machine learning salary trends shaping 2025. Explore how experience, location, and industry impact earnings, and learn why AI careers continue to offer strong growth and global opportunities for skilled professionals

An AI health care company is transforming diagnostics by applying generative AI in radiology, achieving a $525M valuation while improving accuracy and supporting clinicians

Curious how LLMs learn to write and understand code? From setting a goal to cleaning datasets and training with intent, here’s how coding models actually come together

Can small AI agents understand what they see? Discover how adding vision transforms SmolAgents from scripted tools into adaptable systems that respond to real-world environments

Discover the exact AI tools and strategies to build a faceless YouTube channel that earns $10K/month.
How IBM expands AI features for the 2025 Masters Tournament, delivering smarter highlights, personalized fan interaction, and improved accessibility for a more engaging experience

How serverless GPU inference is transforming the way Hugging Face users deploy AI models. Learn how on-demand, GPU-powered APIs simplify scaling and cut down infrastructure costs
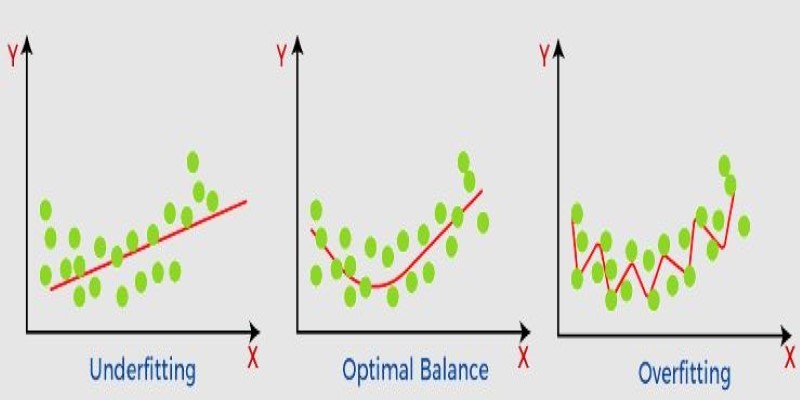
What non-generalization and generalization mean in machine learning models, why they happen, and how to improve model generalization for reliable predictions

Learn how to compare two regression models with statistical significance for accuracy, reliability, and better decision-making

Learn the difference between SSH and Telnet in cyber security. This article explains how these two protocols work, their security implications, and why SSH is preferred today