Advertisement
The rise of large language models (LLMs) has shifted how teams interact with their data. These models can answer questions, summarize documents, and automate tasks—but only when they have access to the right information. That’s the gap many businesses face. LLMs, by default, don’t know your company’s internal systems, knowledge base, or workflows.
You need a reliable way to bridge that gap. That’s where the Model-Connection Platform (MCP) comes in. It offers a direct, efficient, and secure method to plug LLMs into your internal data sources without rewriting your infrastructure or overcomplicating your tech stack.
The Model-Connection Platform (MCP) is a software layer that sits between your internal data systems and a language model. Its main job is to handle data access, formatting, routing, and context packaging, so LLMs can use your proprietary information in real-time. Think of MCP as a translator and traffic controller rolled into one.
At its core, MCP doesn’t replace any part of your existing systems—it connects them. Whether your data lives in a database, document store, CRM, intranet, or internal APIs, MCP can find it, fetch it, and deliver it to the model in a way it can understand and reason about.
But it’s not just about getting data into the hands of an LLM. It’s about doing it responsibly, at speed, and with enough context to reduce hallucinations and ensure accurate outputs. This is what makes MCP more than just a data pipeline.
Most LLMs don’t have persistent memory or native access to private data. You can’t just upload a terabyte of documents and expect reliable answers. Simply feeding everything into a model won’t work either—context windows are limited, and irrelevant information leads to low-quality responses.
The Model-Connection Platform handles this challenge by doing four key things:

MCP first understands the user’s question or task. Then it pulls only the relevant information from your data sources. This is often done using hybrid search (semantic and keyword-based), metadata filtering, or query rewriting. That way, the model works with only what it needs.
Once the relevant documents or records are retrieved, MCP formats them into structured prompts tailored for LLM input. This often includes titles, snippets, metadata, and timestamps. It knows how to stay within the model’s context window while keeping the right amount of detail.
MCP supports fine-grained permissions. It checks whether the model—or the user prompting it—is allowed to access the data in question. This is crucial in business environments with strict security requirements.
After the model responds, MCP can clean, verify, or reformat the output before it’s returned to the user or system. This ensures results are aligned with business rules, templates, or tone-of-voice standards.
By doing all of this in the background, MCP makes the experience feel seamless. Users can simply ask a question in natural language, and the model responds with answers that reflect live company knowledge.
The real strength of the Model-Connection Platform is its flexibility. Since it connects LLMs to internal data without requiring major architecture changes, it works across departments and industries.

For support teams, MCP can fetch accurate answers from internal knowledge bases, previous ticket logs, or technical documentation. When a customer asks a question, the support agent (or bot) gets context-aware help instantly—without needing to search manually.
In sales, MCP can combine data from a CRM, past email threads, and product specs to help teams craft personalized proposals or answer prospect questions quickly. It ensures that what the model suggests is not based on guesses, but on actual company history and offerings.
Legal teams can use it to analyze contracts, policies, or compliance documents. MCP helps LLMs connect to case-specific details so that summaries or redlines reflect the right clauses, exceptions, or local regulations.
In operations, MCP powers smart automation by giving models access to internal SOPs, data dashboards, or historical trends. This can be used for daily reports, process analysis, or anomaly detection—all without relying on predefined scripts.
Because it’s modular, MCP works whether your data lives in cloud platforms like Google Drive, internal SQL databases, third-party SaaS tools, or even in air-gapped environments. That versatility allows organizations to experiment with LLMs without committing to a full migration or rebuild.
There’s growing interest in using LLMs in the enterprise, but hesitation remains around security, performance, and integration cost. Many companies want to connect LLMs to internal data without building a parallel IT system or giving up control.
That’s why Model-Connection Platforms are gaining traction. They act as a thin layer of glue that lets companies integrate natural language interfaces into existing tools. They’re scalable—once one team adopts MCP, others can follow without starting from scratch.
Instead of making teams change how they store or structure data, MCP adapts to existing formats. It supports connectors, adapters, and plugins that let developers define how each data source is queried, cleaned, and injected into prompts. This gives technical teams control while keeping the end-user experience simple.
Another reason MCPs are becoming standard is their auditability. Everything the LLM sees, uses, and returns can be tracked. That helps with compliance, debugging, and building trust. You can see which data sources were accessed, how long the response took, and what prompt was sent—without guessing.
This matters in regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, or insurance, where even experimental AI must meet operational standards. MCP makes it possible to connect LLMs to internal data while staying within governance frameworks.
Model-Connection Platforms (MCPs) are becoming essential as businesses adopt LLMs. They solve a key challenge—how to connect LLMs to internal data securely and efficiently, without overhauling existing systems. MCPs handle access, routing, and prompt building, turning general-purpose models into practical tools for everyday work. By removing friction and preserving control, MCPs let teams get real value from AI. It's not just about smart models—it’s about using them with the right data at the right time.
Advertisement

Know how AI transforms Cybersecurity with fast threat detection, reduced errors, and the risks of high costs and overdependence
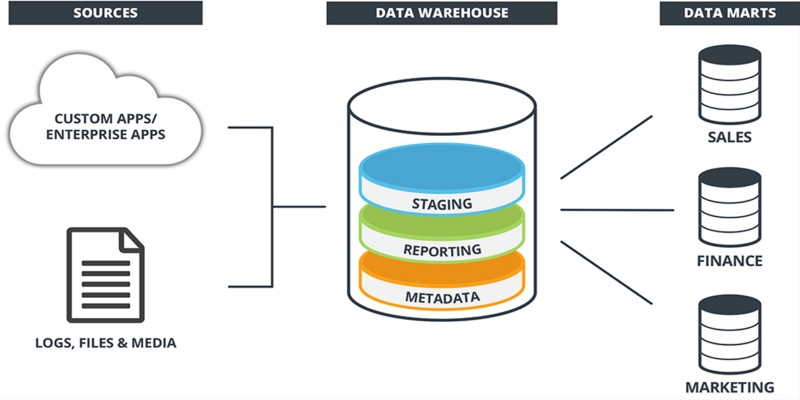
Learn what a data warehouse is, its key components like ETL and schema designs, and how it helps businesses organize large volumes of data for fast, reliable analysis and decision-making

An AI health care company is transforming diagnostics by applying generative AI in radiology, achieving a $525M valuation while improving accuracy and supporting clinicians

Nvidia is set to manufacture AI supercomputers in the US for the first time, while Deloitte deepens agentic AI adoption through partnerships with Google Cloud and ServiceNow

Learn how the healthcare, marketing, finance, and logistics industries apply generative AI to achieve their business goals

Discover a clear SQL and PL/SQL comparison to understand how these two database languages differ and complement each other. Learn when to use each effectively

What's fueling the wave of tech layoffs in 2025, from overhiring during the pandemic to the rise of AI job disruption and shifting investor demands

What's changing inside your car? A new AI platform is making in-car assistants smarter, faster, and more human-like—here's how it works

How does an AI assistant move from novelty to necessity? OpenAI’s latest ChatGPT update integrates directly with Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace—reshaping how real work happens across teams

AI saved Google from facing an antitrust breakup, but the trade-offs raise questions. Explore how AI reshaped Google’s future—and its regulatory escape

Discover the best AI art generator tools available today. Learn how you can create AI art from text prompts using powerful, easy-to-use platforms suited for beginners and pros alike

Discover the exact AI tools and strategies to build a faceless YouTube channel that earns $10K/month.