Advertisement
People are learning more about themselves every day thanks to small devices on their wrists and clever software working quietly behind the scenes. Wearable technology has grown far beyond counting steps or showing notifications. Researchers have now developed a machine learning algorithm capable of predicting mood changes based on the data collected by these wearables.
This approach blends psychology, physiology, and data science to forecast emotional shifts before they even become noticeable to the wearer. The implications stretch from personal well-being to mental health care, making it a step forward in how technology supports human needs.
Wearable devices are equipped with sensors that track heart rate, sleep patterns, skin temperature, activity levels, and even subtle changes in blood oxygen. Most people know them for fitness tracking or sleep monitoring, but the data streams they generate paint a far more detailed picture of what’s happening in the body throughout the day. Changes in heart rate variability, for example, can indicate stress or fatigue. Sleep quality and physical activity are strongly linked to mood and mental states. Skin conductance, which measures how much you sweat, can reflect how stressed or calm you are in real time.
These signals are collected passively, meaning there’s no active input required from the user. That passive collection makes the process seamless and unobtrusive. Over time, these metrics create a unique baseline for each person. Deviations from this baseline often correspond to shifts in how someone feels, even before they’re fully aware of it themselves. This is where machine learning comes into play — finding patterns too subtle or complex for humans to recognize without help.
The machine learning algorithm behind this predictive ability relies on training itself on large amounts of data. In the initial stages, the algorithm learns what normal looks like for each individual. Since everyone has different baselines and different ways of reacting to stress, fatigue, and happiness, personalization is key. The system then compares incoming real-time data to this baseline and detects patterns linked to previous mood shifts.

For example, a slight drop in sleep quality, combined with an elevated resting heart rate and reduced physical activity over a couple of days, might precede a low mood. Similarly, increased movement and steady heart rate variability could signal a more positive emotional period ahead. The algorithm does not simply track one factor, but rather examines the interplay between multiple data points over time. It also gets better the longer it observes a person, as the dataset becomes more nuanced and the model refines its predictions.
Unlike traditional mental health assessments, which depend on subjective self-reporting, this method offers an objective measure of changes in mood state. It detects subtle physiological shifts that may not feel obvious to the individual yet. This can be particularly useful for people with mood disorders, such as depression or bipolar disorder, where early warning of a downturn can help them and their caregivers take preventive action.
Predicting mood changes has clear benefits for mental health care. Individuals struggling with anxiety or depression often experience fluctuations that can feel sudden or unpredictable. With a wearable device and a machine learning algorithm monitoring their patterns, they can receive early warnings when their data suggests a downward trend. That gives them time to adjust routines, seek support, or take other actions before a full episode develops.
Therapists and doctors could also use this data to supplement their clinical work. Rather than relying solely on what a patient remembers during an appointment, they can review objective trends over weeks or months to better understand triggers and progress. In group settings, such as schools or workplaces, aggregated and anonymized data could help identify when many people are under stress and might benefit from additional support.
For the general population, even without a mental health diagnosis, mood prediction can help manage everyday stress. Knowing when you're likely to feel low or irritable allows you to plan challenging tasks when you're in a better headspace, thereby improving productivity and emotional well-being. Athletes and performers may use similar insights to optimize their mental readiness for big events. The potential for positive habit formation is significant, as people can see how sleep, diet, exercise, and stress management directly affect their mood.
While the technology offers promise, it raises questions about privacy and consent. Mood and mental health data are highly sensitive, and users need to understand who has access to their information and how it is used. Companies developing such tools must prioritize security and transparency, giving people control over their data. Wearables already collect vast amounts of personal information, and adding emotional state predictions only makes responsible handling more urgent.

Looking ahead, the algorithm can become more accurate by incorporating additional types of data. Combining wearable data with voice tone analysis, facial expression tracking, or smartphone usage patterns could enrich the model’s understanding of mood. Advances in sensor technology may also allow wearables to measure new biomarkers, such as hormonal levels, in a noninvasive way. Machine learning itself is evolving, and more sophisticated models may be able to differentiate between short-term fluctuations and more serious, longer-term mood changes.
This kind of integration between technology and personal well-being illustrates how everyday devices can move beyond convenience into meaningful support. As people become more comfortable with wearables as tools for health rather than just gadgets, the willingness to use them for mental health may grow as well. The machine learning algorithm’s ability to predict mood changes shows how far data-driven insights can go toward helping people understand and care for themselves better.
Machine learning and wearable technology combine to offer a personal, practical way to track mood changes early. By analyzing data from everyday devices, predictive algorithms identify shifts before they worsen, giving people time to act. This fusion of sensors and personalized patterns supports mental health management and helps anyone better understand their mind-body connection. Wearables are evolving from fitness trackers into thoughtful companions that assist in maintaining emotional balance over time.
Advertisement

Learn the top 5 AI change management strategies and practical checklists to guide your enterprise transformation in 2025.

How LLMs and BERT handle language tasks like sentiment analysis, content generation, and question answering. Learn where each model fits in modern language model applications

Wondering whether a data lake or data warehouse fits your needs? This guide explains the differences, benefits, and best use cases to help you pick the right data storage solution

Learn how to compare two regression models with statistical significance for accuracy, reliability, and better decision-making

Struggling to connect tables in SQL queries? Learn how the ON clause works with JOINs to accurately match and relate your data
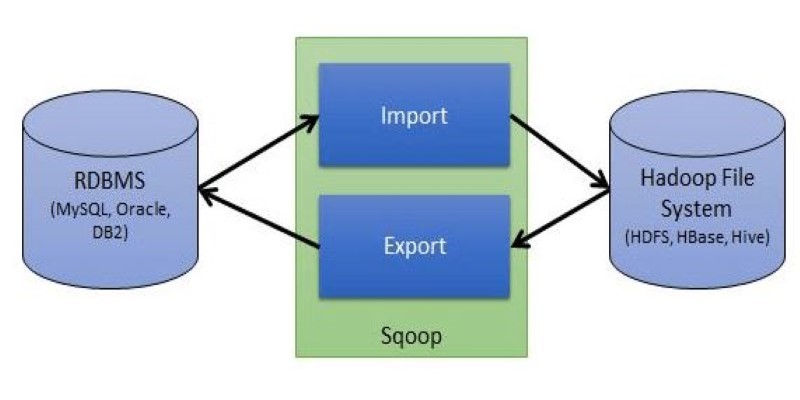
Explore Apache Sqoop, its features, architecture, and operations. Learn how this tool simplifies data transfer between Hadoop and relational databases with speed and reliability
Learn how integrating feature selection into model estimation improves accuracy, reduces noise, and boosts efficiency in ML

Writer unveils a new AI platform empowering businesses to build and deploy intelligent, task-based agents.

How a machine learning algorithm uses wearable technology data to predict mood changes, offering early insights into emotional well-being and mental health trends
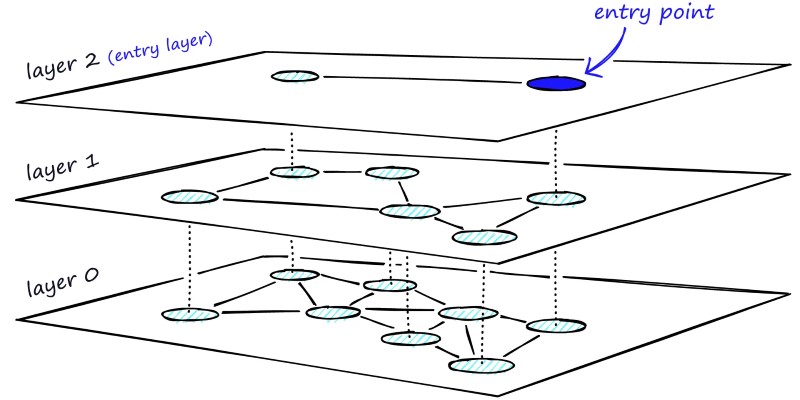
Learn how HNSW enables fast and accurate approximate nearest neighbor search using a layered graph structure. Ideal for recommendation systems, vector search, and high-dimensional datasets

Can AI really help a Formula One team build faster, smarter cars? With real-time data crunching, simulation, and design automation, teams are transforming racing—long before the track lights go green

How using open-source AI models can give your startup more control, lower costs, and a faster path to innovation—without relying on expensive black-box systems